CURVES in the PLANE
1. Line segment
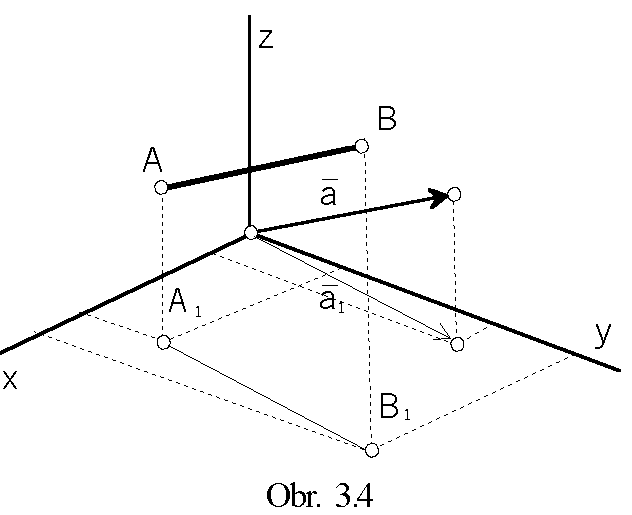
Line segment can be created by translating a given point in the direction of a given vector (Fig. 3.4).

Synthetic representation: (A, Tp(u))
Analytic representations:
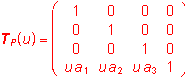 , for uÎ<0,1>
, for uÎ<0,1> Interior properties of the modelled figure:
r´(u) = (a1, a2, a3, 0)
![]()
r´´(u) = 0 r´(u) ´ r´´(u) = 0 çr´(u) ´ r´´(u)ç = 0 r´´´(u) = 0
Frenet-Serret trihedron in the point P(u), uÎ<0,1> does not exist.
![]() b(u)=0 n(u)=0
b(u)=0 n(u)=0
1k(u)=0 1r=
![]() 2k(u)=0
2k(u)=0
All points on the line segment are points of inflection, any plane passing through the line segment is the osculating plane.
Line segment (line) is the curve of zero both, the first and the second curvatures.
2. Circular arc (circle)
Circular arc can be created by revolving the point about the line o by angles from the interval <0,a>.
For a=2p there is created the circle (Fig. 3.5).
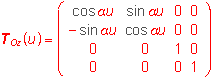 , for u
, for uInterior properties of the modelled figure:
r´(u)=(-asin au, acos au, 0, 0) ç r´(u)ç =
![]()
r´´(u)= -a2( acos au, asin au, 0, 0)
r´´´(u)= -a3(-asin au, acos au, 0, 0)
r´(u) ´ r´´(u) = (0, 0, a3a2, 0) ç r´(u) ´ r´´(u)ç = a3a2 [r´(u) r´´(u) r´´´(u)]=0
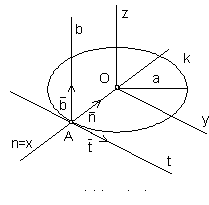
Frenet-Serretov trihedron in the point P(u), u Î<0,1>
t(u)= (-sin au, cos au, 0, 0) b(u)=(0, 0, 1, 0) n(u)= ( -cos au, -sin au, 0, 0)
1k(u)=1/a 1r(u)=a 2k(u)=0
Circle is a curve in the plane, which is self-osculating circle at any point, radius of the circle is the radius of the first curvature.
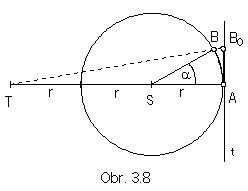
Rectification methods of the circular arc length
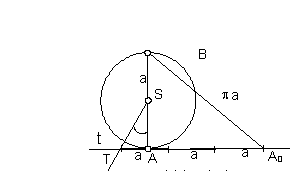
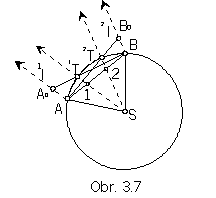 D'Ocagne (central angle of the arc AB is in the interval (30°, 60°))
D'Ocagne (central angle of the arc AB is in the interval (30°, 60°))
(Fig. 3.7).
1. |A1|=|12|=|2B|
2. S1ÇAB=1T (S2ÇAB=2T)
3. AÎ1l, 1l // S1 (BÎ2l, 2l // S2)
4. 1lÇB1T=A0, |A0B|=|AB| (2lÇA2T=B0, |AB0|=|AB)
3. Ellipse
Ellipse can be created as the affine image of the circle (Fig. 3.9).
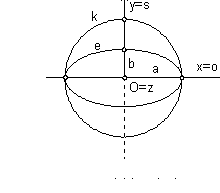
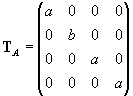
Interior properties of the modelled figure:
r´(u)=a(-asin au, bcos au, 0, 0) çr´(u)ç =a
![]()
r´´(u)= -a2(acos au, bsin au, 0, 0) r´´´(u)= -a3(-asin au, bcos au, 0, 0)
[r´(u) r´´(u) r´´´(u)]=0 r´(u) ´ r´´(u) = (0, 0, a3ab, 0) çr´(u) ´ r´´(u)ç =a3ab
Frenet-Serretov trihedron in the point P(u), uÎ<0,1>
t(u)=(-asin au, bcos au, 0, 0)/d b(u)=(0, 0, 1, 0) n(u)= (bcos au, -asin au, 0, 0)/d
1k(u)=ab/d3 1r(u)=d3/ab 2k(u)=0
4. Parabola
Parabola can be created as the collinear image of the circle (Fig. 3.10).
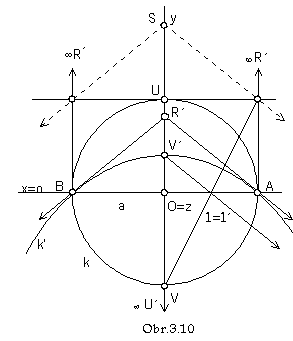
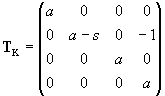
Ideal point of the parabola is the point P(1/4).
Point V=(0, -a, 0, 1) is mapped to the vertex of parabola
V´=V.TK=(0, s-a, 0, 2)=(0, (s-a)/2, 0, 1)=r(3/4)=
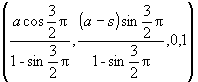
Ideal point
![]() R of intersection of tangent lines to the circle k in its invariant points A, B is mapped to the real point R´,
R of intersection of tangent lines to the circle k in its invariant points A, B is mapped to the real point R´,
in which the tangent lines to the collinear parabola k´intersect.
5. Hyperbola
Hyperbola can be created as the collinear image of the circle (Fig. 3.11).
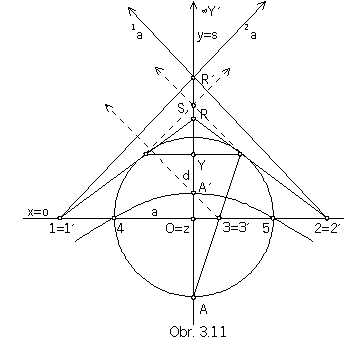
Synthetic representation: (k, TK)
Analytic representations:
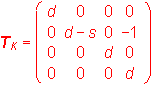
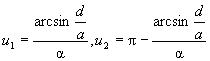 .
. Ideal points on hyperbola are P(u1), P(u2).
Point A=(0, -a, 0, 1) is collinearly mapped to the vertex of hyperbola
![]() ,
,
point B=(0, a, 0, 1) to the other one (not viewed) vertex
![]() .
.