Euler's Method for systems of ordinary differential equations using Mathematica
![]()
Anotation

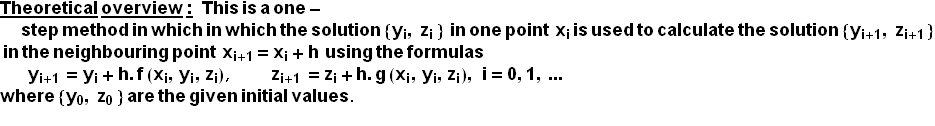
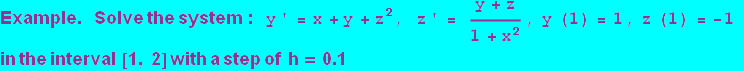
![]()
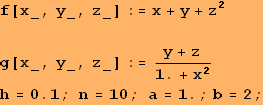
![]()

![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()

| 1. | 1. | -1. | ||
| 1.1 | 1.3 | -1. | 3. | 0. |
| 1.2 | 1.64 | -0.986425 | 3.4 | 0.135747 |
| 1.3 | 2.0213 | -0.959639 | 3.81303 | 0.267858 |
| 1.4 | 2.44552 | -0.920172 | 4.24221 | 0.394671 |
| 1.5 | 2.91475 | -0.86864 | 4.69224 | 0.515322 |
| 1.6 | 3.43168 | -0.805683 | 5.16928 | 0.629572 |
| 1.7 | 3.99976 | -0.731919 | 5.6808 | 0.737639 |
| 1.8 | 4.6233 | -0.647913 | 6.23546 | 0.840061 |
| 1.9 | 5.30761 | -0.554154 | 6.8431 | 0.937592 |
| 2. | 6.05908 | -0.451042 | 7.5147 | 1.03112 |
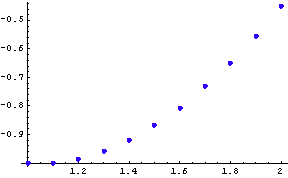
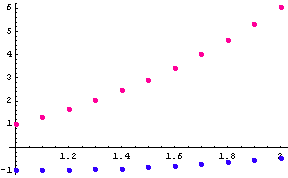
Conclusion: The solution derived using the Euler's method is in the form of a table of the variable functions y(x), z(x), as shown in the second and third column of the table above, respectively. Since the априорна error of the method is О(![]() ) and here h=0.1, then these solutions must be taken rounded only to the second symbol after the decimal point.
) and here h=0.1, then these solutions must be taken rounded only to the second symbol after the decimal point.
Graphic of the solution

![]()
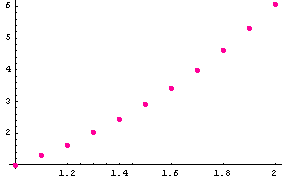
![]()

![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
| Created by Wolfram Mathematica 6.0 (22 September 2008) |