Euler's-Cauchy Method using Mathematica
![]()
Аnotation


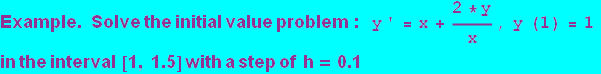
![]()
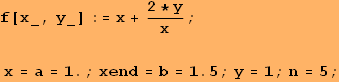
![]()
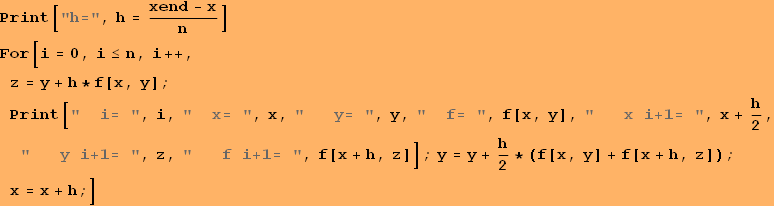
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
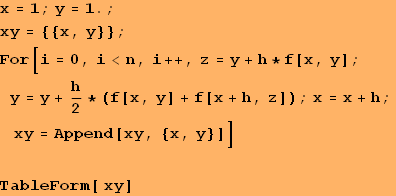
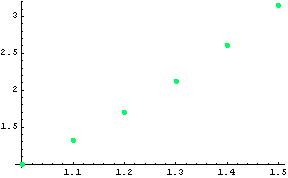
| 1 | 1. |
| 1.1 | 1.32318 |
| 1.2 | 1.69795 |
| 1.3 | 2.12606 |
| 1.4 | 2.60911 |
| 1.5 | 3.1486 |
Conclusion: The solution derived using the modified Euler's-Cauchy method is in the form of a table of the variable function y(x), as shown in the second column of the table above. Since the global apriori error of the method is О(![]() ) and here h=0.1, then these solutions must be rounded to only two signs after the decimal point.
) and here h=0.1, then these solutions must be rounded to only two signs after the decimal point.
Graphic of the solution
![]()
![]()
![]()
| Created by Wolfram Mathematica 6.0 (22 September 2008) |